Architecture
Indexify is a complex system that has many different pieces. To help both users and developers of Indexify build a mental model of how it works, this page documents the system architecture.
Advanced Topic
This page covers the technical details of Indexify. You do not need to understand these details to use Indexify effectively. The details are documented here for those who wish to learn about them without having to go spelunking through the source code.
The architecture of Indexify is shaped with the following requirements -
- Support ingesting millions of unstructured data and continuously running extraction and indexing pipelines in real time.
- Horizontally scale with more ingested data so applications don't need to switch to a more serious framework as they become mature.
- Time to extraction be at most a few seconds after data is ingested so that we can support LLM applications requiring business decisions related to the real world where things change frequently.
- Run extraction pipelines across various hardware platforms - GPUs, TPUs, and CPUs. Run more compute-intensive parts of a pipeline that use deep learning models on GPUs, while less compute-intensive processes on CPU.
- Support auto-scaling so that compute nodes are released when there is no data to process.
- Support spot instances - if work is not finished and extractors are removed, it's restarted elsewhere on the cluster.
- Support multi-cloud and federated deployments of data planes. This allows running a pipeline across data centers with more GPU capacity while data and applications reside on another cloud.
- Local first experience to make it easy to prototype and test applications. Let's face it: every journey starts with a developer's laptop.
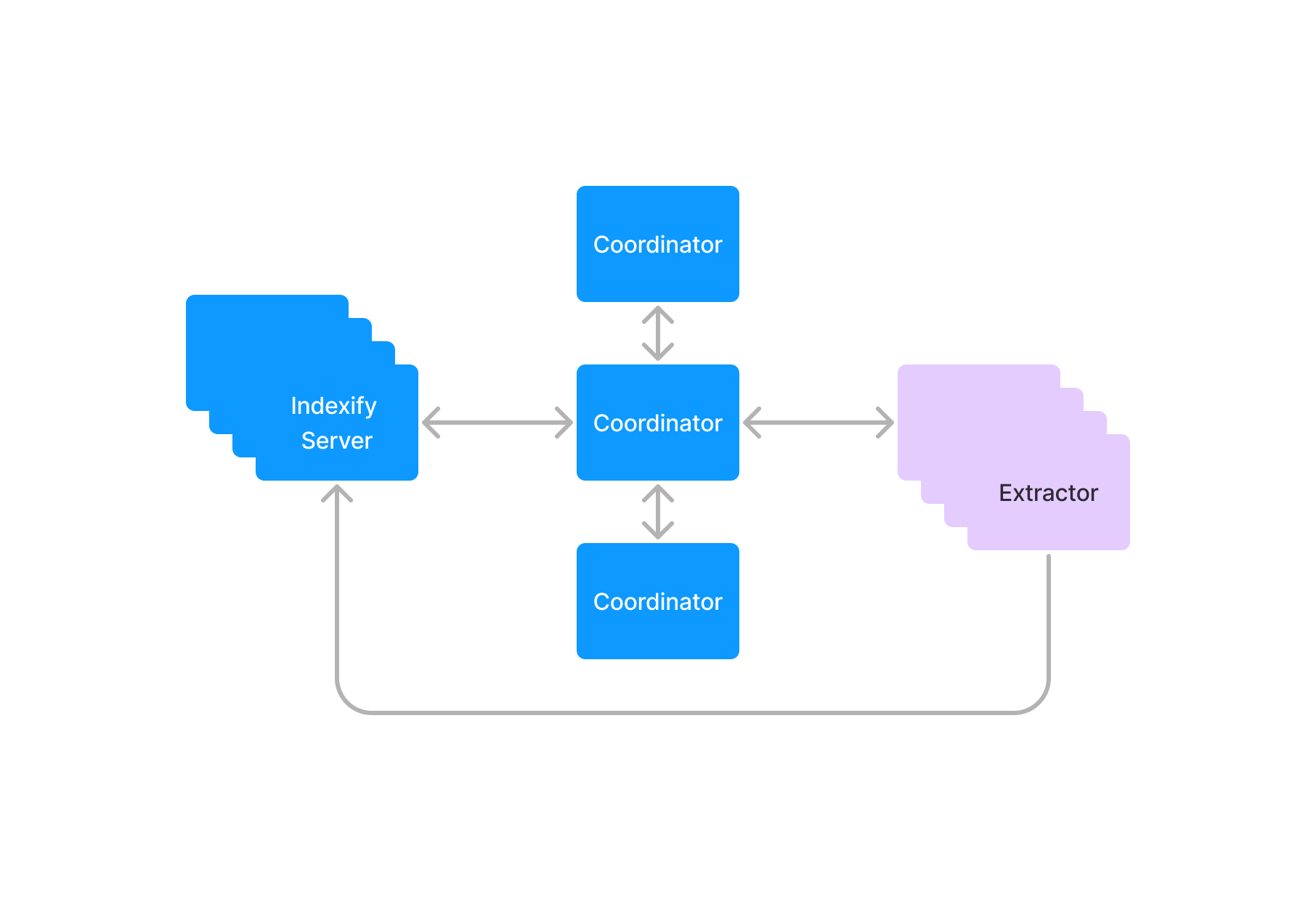
Indexify is composed of two main components - - Indexify Server comprises the ingestion system and the task scheduler for running extraction. - Indexify Extractors runs models or algorithms to transform or extract structured data or embed it from unstructured data.
Indexify Server
Indexify Server is composed of two primary services. They are run together when Indexify runs in the development mode. High-scale production use cases can be deployed separately to scale them out horizontally and for high availability.
Coordinator
The Coordinator is a blazing-fast task scheduler that creates 1000s of tasks every second whenever data is ingested. It evaluates the extraction policies and allocates tasks to extractors. The Coordinator doesn't have any external dependencies and uses a replicated state machine under the hood to replicate itself across many machines. This design allowed us to build an entirely reactive scheduler to evaluate 1000s of extraction policies and content and schedule tasks.
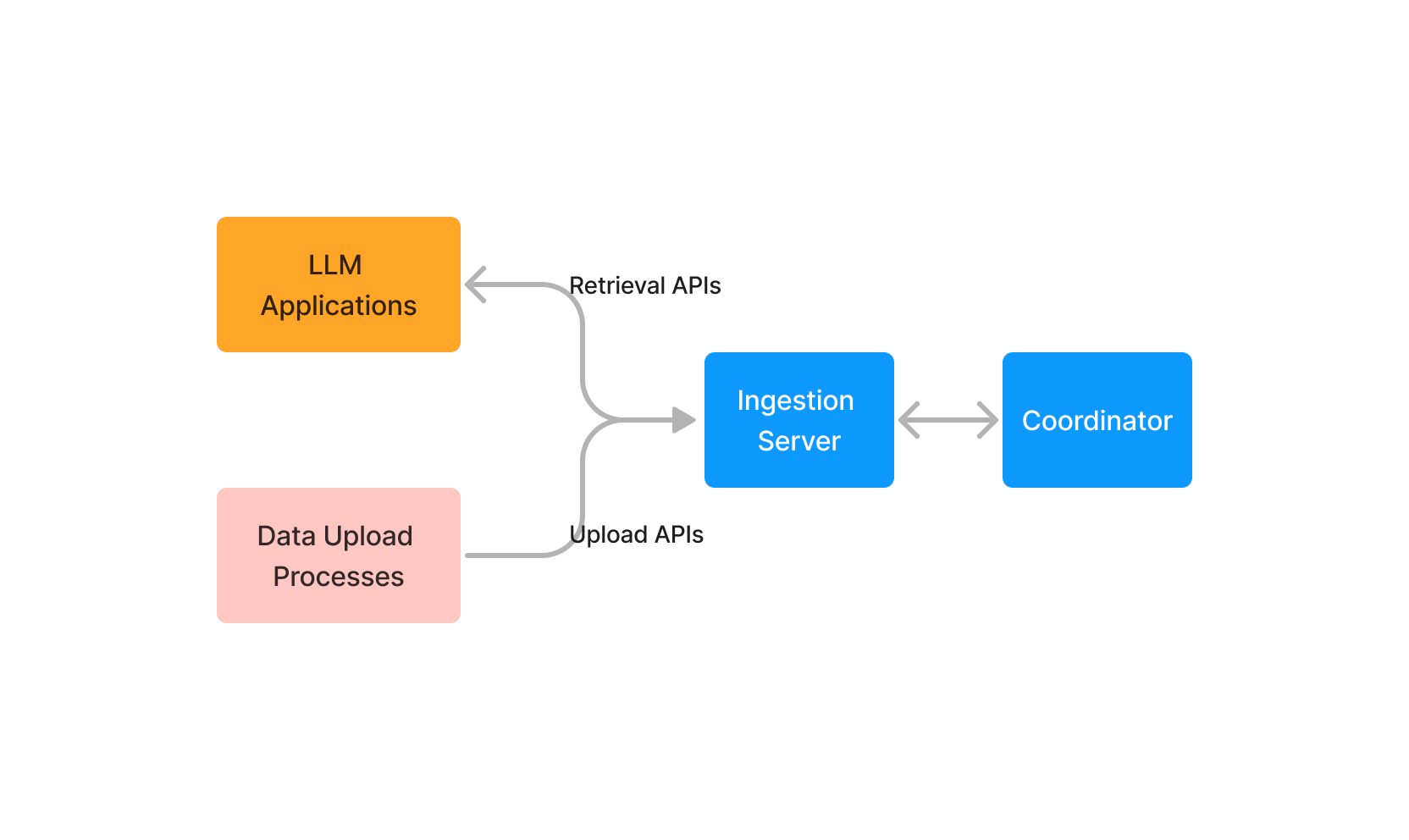
Ingestion Server
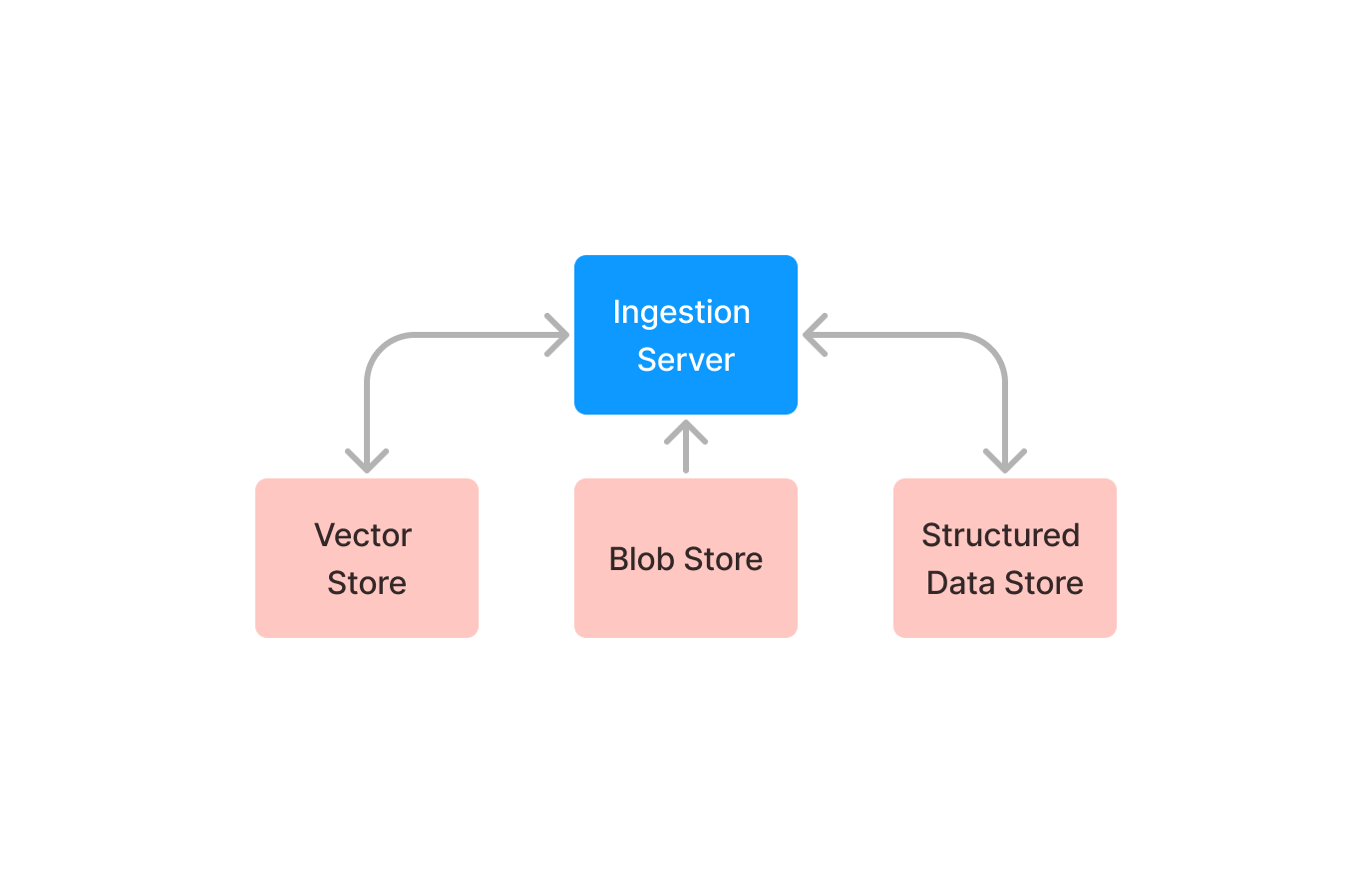
Ingestion Server exposes HTTP APIs for clients to upload content into Indexify. They expose retrieval APIs also for clients to retrieve extracted data, or search over vector indexes or query structured data using SQL. Ingestion server also ingests extracted embedding, structured data from extractors and stores them in the appropriate storage systems. Ingestion APIs sits on top of storage systems -
- Blob Stores - Ingested unstructured data are stored on blob stores(S3, file system, etc.). Using blob stores allows Indexify to work with large blobs at any scale. It can work with videos, large PDF files, and millions of such files.
- Vector Stores - Writes extracted embedding to vector stores.
- Structured Stores - Writes semi-structured data as JSON in structure data stores like PostGres and SQLite.
The ingestion server is entirely stateless. It can be scaled horizontally based on the data ingestion rate. It strictly does only I/O and thus can be run on cheap hardware in production. Ingestion servers use the Coordinator to store metadata about ingested content.
Extractors
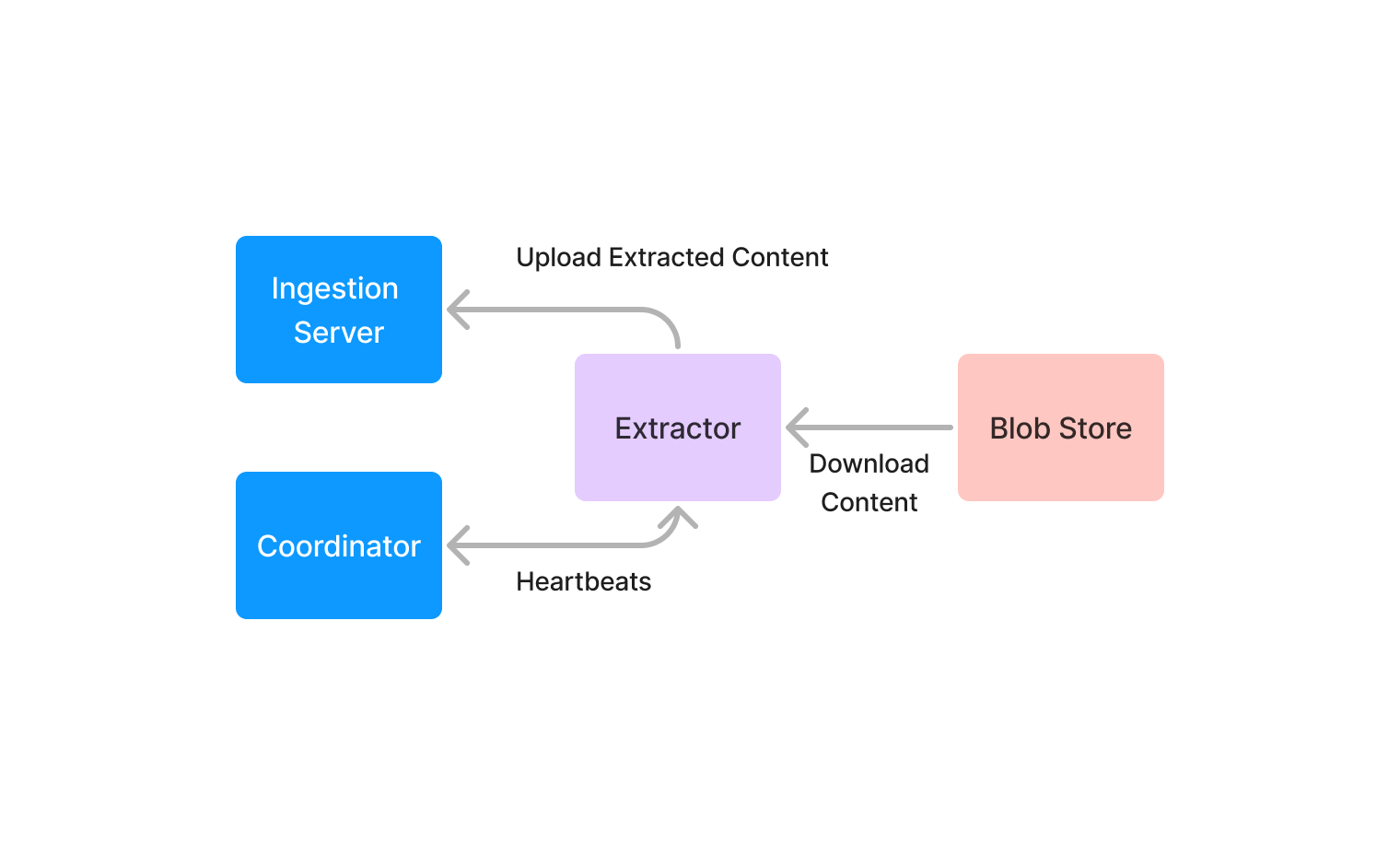
Extractors are compute functions that transform unstructured data or extract information from them. Any model or algorithm for processing unstructured data can be implemented as an extractor by implementing an abstract class, part of the extractor SDK. They run on any hardware, and a single Indexify deployment can support 10s of 1000s of extractors in a single cluster.
They communicate with the Coordinator over a bi-directional Grpc stream. When they start up, they register their capability to the Coordinator and send heartbeats periodically. When the Coordinator has some tasks that require running on an extractor, it sends the Tasks to the extractor on the heartbeat stream. The extractor downloads the content from the storage system and then runs its compute function. After tasks are completed, any extracted data is uploaded back to the ingestion server, and the task outcome is sent to the Coordinator over the heartbeat stream.
Deployment Layout
Indexify can run locally with all the components running on a laptop. It can be deployed in a distributed manner as well, in high-availability and scale out modes.
Local Mode
 In the local mode coordinator and ingestion server is started in the same process. Embedding are stored in LanceDB, structured data is stored in sqlite and ingested files are stored in the local disk. All the components are started right in the process, so no other dependencies are required to run Indexify locally.
In the local mode coordinator and ingestion server is started in the same process. Embedding are stored in LanceDB, structured data is stored in sqlite and ingested files are stored in the local disk. All the components are started right in the process, so no other dependencies are required to run Indexify locally.
All the extractors are started in a single process and communicates with Indexify server through ports on localhost.
Production
The production deployment depends on scale, and high availability requirements. The extreme scale and high availability mode can be achieved by running multiple ingestion servers, three or five copies of coordinators, and as many extractors as needed based on the throughput of extraction.